
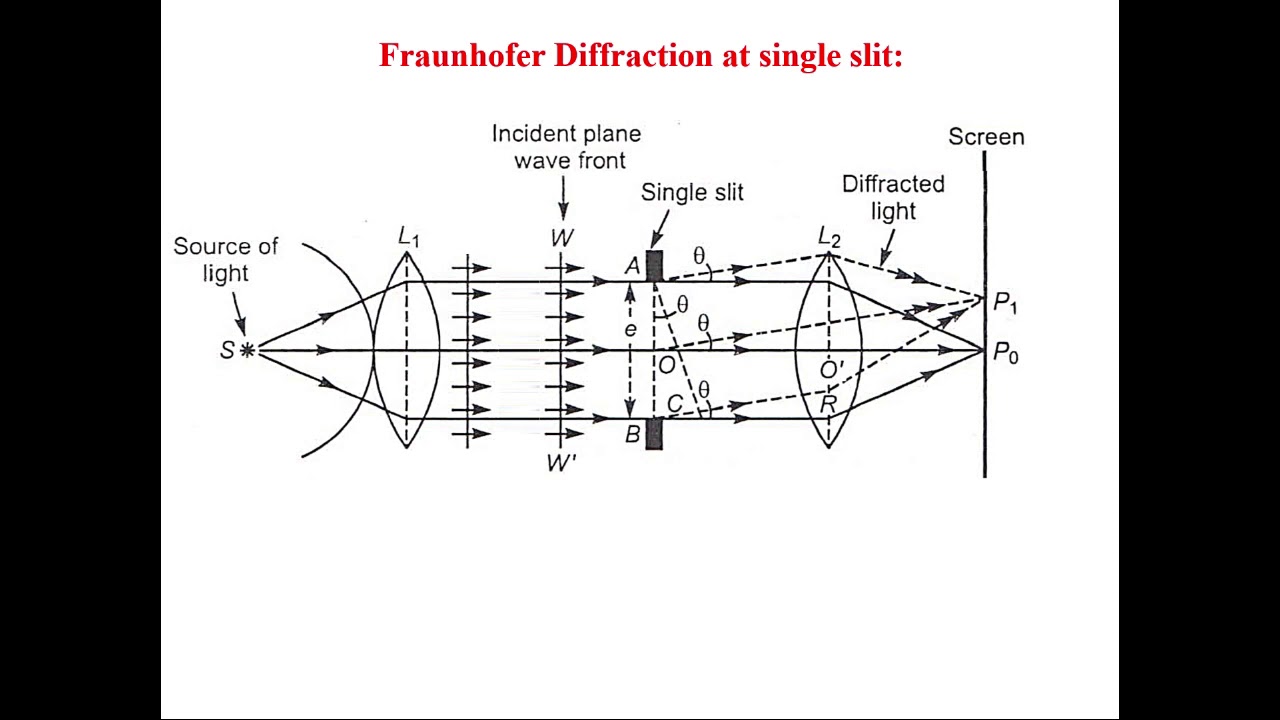
In figure, suppose BN = λ and θ = θ 1 then sin θ 1 = `lambda/"a"` BN is the path difference between secondary waves coming from A and B.
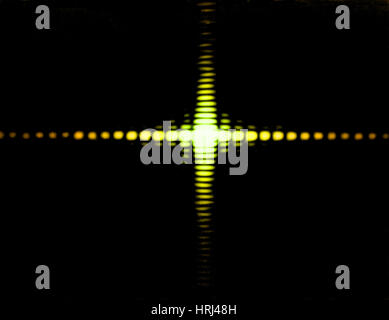

According to Huygens’ principle, each and every point of the slit acts as a source of secondary wavelets, spreading in all directions.Let D be the distance between the slit and the screen.The screen is kept in the focal plane of the lens and is perpendicular to the plane of the paper.The diffracted light is focused by a converging lens L, on a screen XY.It is illuminated by a parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength λ i.e., a plane wavefront is an incident on AB. The slit can be imagined to be divided into extremely thin slits or slit elements. Consider a narrow slit AB of width ‘a’, kept perpendicular to the plane of the paper.Fraunhofer diffraction due to single slit:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
